If you want to call a web service from a Java Spring application, the best way to go around the problem is (in my opinion) by creating:
- A POJO for the request and a POJO for the response. You could avoid these by working directly with JSON strings but I think this could go wild.
- A bean that invokes the web service, with the password and user as attributes. This bean will use the previous POJO's to build the invocation to the ws.
Request and Response POJO's
In my example I have a web service that takes an object with the webcam parameters (number of seconds to wait until the webcam detects movement), and a response object with the images obtained by the server.
This will be my request:
\src\main\java\com\hjbello\restfulws\RequestCapture.java
Be aware that you will need the following dependencies in your pom.xml file:
in the Getting Started Spring tutorial you have a complete example regarding GET methods.
\src\main\java\com\hjbello\restfulws\RequestCapture.java
package com.hjbello.restfulws; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties; @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public class RequestCapture { private int seconds; public RequestCapture(int seconds) { super(); this.seconds = seconds; } public int getSeconds() { return seconds; } public void setSeconds(int seconds) { this.seconds = seconds; } public RequestCapture() { super(); } }
And this the response:
\src\main\java\com\hjbello\restfulws\CapturedMovement.java
\src\main\java\com\hjbello\restfulws\CapturedMovement.java
package com.hjbello.restfulws; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Date; @JsonIgnoreProperties(ignoreUnknown = true) public class CapturedMovement { private String dateOfCapture; private ArrayList<String> imagesPath; private ArrayList<byte[]> imagesBase64; public String getDateOfCapture() { return dateOfCapture; } public void setDateOfCapture(String dateOfCapture) { this.dateOfCapture = dateOfCapture; } public ArrayList<byte[]> getImagesBase64() { return imagesBase64; } public void setImagesBase64(ArrayList<byte[]> imagesBase64) { this.imagesBase64 = imagesBase64; } public CapturedMovement(String dateOfCapture, ArrayList<byte[]> imagesBase64) { super(); this.dateOfCapture = dateOfCapture; this.imagesBase64 = imagesBase64; } public CapturedMovement() { super(); } public ArrayList<String> getImagesPath() { return imagesPath; } public void setImagesPath(ArrayList<String> imagesPath) { this.imagesPath = imagesPath; } }
Invoker
Now we create the bean that we will autowire every time we need to invoke the restful web service in our application
\src\main\java\com\hjbello\restfulws\WebcamRestWS.java
package com.hjbello.restfulws; import org.apache.http.auth.AuthScope; import org.apache.http.auth.UsernamePasswordCredentials; import org.apache.http.impl.client.BasicCredentialsProvider; import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpClient; import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.client.ClientHttpRequestFactory; import org.springframework.http.client.HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; @Component public class WebcamRestWS { private String url = "http://localhost:8080/capture/"; private String user = "user"; private String password = "1234"; public CapturedMovement invokeWecamRestWS ( RequestCapture requestCapture) throws JsonProcessingException{ //First we prepare the authentification DefaultHttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient(); BasicCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new BasicCredentialsProvider(); credentialsProvider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials(user, password)); httpClient.setCredentialsProvider(credentialsProvider); ClientHttpRequestFactory rf = new HttpComponentsClientHttpRequestFactory(httpClient); //Here we convert the request to json, and then to httpEntity ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); String requestCaptureJson = mapper.writeValueAsString(requestCapture); HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); headers.setContentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON); HttpEntity request= new HttpEntity(requestCaptureJson, headers); //We invoke the web service RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(rf); CapturedMovement response = restTemplate.postForObject(url,request, CapturedMovement.class); return response; } }
Be aware that you will need the following dependencies in your pom.xml file:
<!-- Restful web services --> <dependency> <groupId>org.codehaus.jackson</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-jaxrs</artifactId> <version>1.9.13</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.sun.jersey</groupId> <artifactId>jersey-client</artifactId> <version>1.19</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> </dependency>
If you want to invoke a GET method, instead of restTemplate.postForObject you will need something like
CapturedMovement response = restTemplate.getForObject(url, CapturedMovement.class);
in the Getting Started Spring tutorial you have a complete example regarding GET methods.
Tests with JUnit4
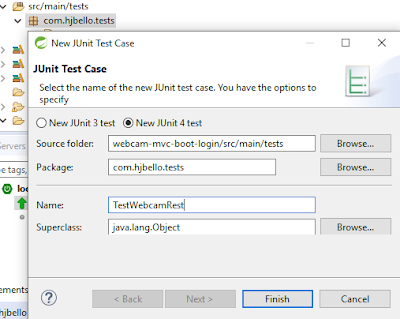
Now that we have our invoker class (or client), we can test it with JUnit4. For that purpose create a src/main/test folder in your classpath and click on New -> JUnit Test Case
\src\main\tests\com\hjbello\tests\TestWebcamRestWS.java
package com.hjbello.tests; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import org.junit.Test; import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException; import com.hjbello.restfulws.RequestCapture; import com.hjbello.restfulws.WebcamRestWS; public class TestWebcamRestWS { @Test public void test() throws JsonProcessingException { WebcamRestWS wr = new WebcamRestWS(); RequestCapture request = new RequestCapture(1); System.out.println("testing web service client"); System.out.println(wr.invokeWecamRestWS(request)); assertNotNull("Asserting that return class is not null", wr.invokeWecamRestWS(request)); } }
To run it we will click on Run As -> JUnit Test
Or alternatively in Run Configurations:
We will see that it Runs OK and it gives us JSON response down in the console:
here you have more info regarding JUnit4.





No comments:
Post a Comment